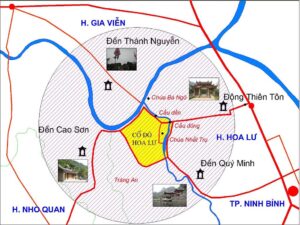
Ninh Binh province has a huge number of unique attractions to satisfy most interests but its spiritual and historical heart is the Ancient City of Hoa Lư. Famed as the capitol of the first united Vietnamese state, the real history of Hoa Lu started millennia ago.
During recent archaeological excavations in the area, researchers have discovered sediments containing the bones and teeth of orangutans and other terrestrial animals. These artifacts have been identified as discarded refuse from the Trang An (Tràng An) culture of the Paleolithic era.
Pre-history
Located in the area bordering the modern districts of Gia Vien and Ninh Binh city, Hoa Lu encompasses an ancient alluvial plain. Nestled at the feet of a mountain range bristling with limestone karsts pockmarked with caves and crisscrossed with an abundance of fresh water streams, it seems tailored for habitation. In such a rich natural environment, it would be more surprising if a rich and varied civilization had not appeared. As it is, Hoa Lu could be argued as the birth place not just of the Vietnamese nation but the Vietnamese people themselves.
As the history of Hoa Lua attests, these early hunters and gatherers migrated to husbandry and agriculture. Clans, alliances and “kingdoms” waxed and waned for millennia without ever forming a central authority or a shared national identity. Eventually, during the Lac Viet-Van Lang- Au Lac period of prehistoric Vietnam, the area was divided into a number of clans loosely aligned with the mystical, almost mythical Hung/Hong Bang Dynasty (2879-258 BC).
An Lac
Renamed An-Lac when the Hung Dynasty was over thrown by a rival warlord in 258-207 BC, the kingdom became fragmented and unable to mount a defend against Han (Chinese) invaders. Eventually overcome by Trieu Da aka Zhao Tuo, a former Qin General, this marked the start of a 1000 years of Chinese domination and the last vestiges of the early Au Lac empire.
Trieu is an interesting character in the history of Hoa Lu. Although ethnically Chinese and a general of southern Chinese armies, he rebelled against both the Qin and Han empires. Eventually, he declared himself emperor of Nanyue, a composite state of two regions in southern China and Au Lac itself. He routed the invading Han army and disposed of all officials remaining loyal to the Chinese empire.
Nanyue
At the time, Nam Viet (Nan Yue) stretched from the Red River delta to the coastal lands as far south as modern-day Da Nang. All good things come to an end and after 100 years of diplomatic and military actions between Nam Viet and the Han Dynasty of southern China, the country was finally conquered by emperor Wudi in around 111 BC.
From the Han Dynasty-Three Kingdoms period to the Northern and Southern Dynasties in China, Hoa Lu was known as Câu Lậu and was a vassal state of the Giao Chi (aka Jiaozhi) district of Southern China. During the Tang Dynasty (618 to 907) it was assigned to the regional government of Changzhou/Guangzhou. When Vietnamese today speak of a thousand years of Chinese occupation, they are referring to this specific period of history and the southern Chinese domination of the old Van Lang- Au Lac empire.
Independence
In 968 buffalo herder, Đinh Bộ Lĩnh united the 12 warlords of Nam Viet and openly rebelled against the Chinese rulers. Successfully routing the Chinese armies, he declared the new state of Đại Cồ Việt, establishing the empire’s first capital in the easily defended karst mountain scape of what is present day Ninh Binh.
It is impossible to overstate the significance of Dinh Bo Linh and the success of what he started over 10 centuries ago. The Dinh Dynasty united the various clans into the nation of Đại Cồ Việt with Hoa Lu as the political, military and administrative center. In many ways Dinh Bo Linh was the father of modern Vietnam and the ancient capital aofHoa Lu is still revered today as the birthplace of the nation.
Dinh Bo’s rule was short (968 to 1009) but the ideals of a free independent state remained strong. The successors to the Dinh, the Tien (early) Le dynasty drove out the remnants of the Song dynasty armies and expanded the kingdom’s territory to Champa (roughly what we know as Central Vietnam today).
The checkered history of Hoa Lu was ascendant. The ancient capitol rapidly became the center for the many diplomatic activities taking place between the court of Đại Cồ Việt and ambassadors from the newly ascendant Northern Song dynasty in China. New buildings were commissioned and old ones upgraded to house diplomatic delegations and to impress on them the majesty and wealth of the new kingdom. But the Tien Le were ultimately an interim government, holding the reins for Lý Công Uẩn (aka Lý Thái Tổ), the founder of the Ly Dynasty (1009-1225).
The Move to Hanoi
In 1010 the new King moved the capital to Thang Long (Hanoi). While Hoa Lu had been a successful bulwark against the Chinese, the new nation needed the massive plains of the Red River to feed and expand its people. Hoa Lu became part of Trường Yên province and Prince Lý Long Bồ of the Ly Dynasty was made Regent. Taking his new role seriously, Lý Long Bồ continued many of the building programs and town improvements. While Hoa Lu was no longer the nation’s capital, it continued to grow and remained well regarded as the southern center of the new state.
With the advent of the Tran Dynasty (1226 to 1400), construction started on the Vu Lam palace on the high ground near Fish Cave (Hang Ca), Tam Coc. Other notable constructions of this time were the Quy Minh temple (Thần Quý Minh ) and the A Nậu pagoda. So while Thang Long remained the capitol, Vu Lam Palace became a southern refuge for the Tran kings, both as a Buddhist retreat and a place to find peace of mind away from Hanoi and the hectic affairs of the dynamic Dai Viet state.
Although the Trần successfully expanded the Đại Việt kingdom south and west into Champa (Khmer) territory, the Mongolian-led Yuan Dynasty of China again threatened them with expansionist designs from the north. The History of Hoa Lu again took a u-turn and became a stronghold and a base against the northern invaders. It was at this time the early South Truong Yen Citadel was reconstructed.
Note:
Hoa Lư has always been an important strategic and defense base, due to its multitude of natural river and mountain barriers. During the Trần Dynasty, Đại Việt continued to serve in this role and used the area as a military base to resist the Mongol-Yuan Dynasty invasions in 1258, 1282–1284, 1285, and 1287–88. Still, several scholars treat the campaigns as a success for China, primarily because Chinese rulers established tributary relations with Đại Việt—even though the Mongols suffered major military defeats.
The Later Ly Dynasty
By the late 1300s, the Tran Dynasty was experiencing constant attacks from the north, internal discontent, and inter-familial rivalry, causing its power and glory to wane. In 1400, Hồ Quý Ly, a Tran general, seized control and founded the Hồ Dynasty, which only lasted from 1400-1406. During his reign, he renamed Dai Viet to Dai Ngu. However, in 1407, Hồ Quý Ly and his son suffered a resounding military defeat at the hands of the Ming Dynasty. The Ming Empire imprisoned them and annexed Đại Việt, ruling the new province for nine years, from 1407 to 1417.
Le Loi, a wealthy landowner from Lam Son in Thanh Hoa took exception to the Chinese rule and began a popular movement of national resistance in 1418. Le Lợi and his resistance movement ousted the Chinese, and the Vietnamese people celebrated him as a national hero. However, the cost was high with a devastated economy and a populace deeply dissatisfied with the old Dynasty. Le Loi (also known as Binh Dinh Vuong aka “Prince of Pacification” ) took control and founded the Later Le Dynasty, taking the name royal name of Le Thai To.
Note: Vietnamese history can be confusing due to the constant renaming provinces, towns, titles and persons. Sometimes a place or a king might go through a dozen or more designations. Where ever possible we have tried to use the most common nomenclature however with a Vietnamese hero of the stature of Le Thai To, with streets throughout Vietnam called both Le Loi and Le Thai To, it is important to know they are all one and the same person, demonstrating just how powerful a figure he is in contemporary Vietnamese history.
A Vietnamese Renaissance
Like the Tran, the Later Le Dynasty kept the name Dai Viet, promoted a sophisticated legal system, funded the arts, literature, and education and increased agriculture output. It is also notable that, at least in the early years, the Le Dynasty strengthened communal land rights, going as far as to instituting a redistribution of land at the expense of the large landowners.
The Dai Viet culture, economy and population flourished under the following 350 year reign of the Later Le but that created its own set of problems. With arable land in the mountainous north unable to meet the needs of such a rapidly growing nation, around 1471 the Le under King Le Thanh Tong (1442-97) turned to the south and westward to begin a series of successful conquests against the declining Khmer (Cambodian) Empire.
This period of great expansion of Dai Viet to the fertile plains of the south continued well into the 18th Century under successive Dynasties, altering the course of Vietnam history forever. Before this expansion, a strong central government and an effective administration ruled Đại Việt.. Such an expansion put great pressure on the system and after the death of Le Thanh Tong, the Dai Viet Empire fell into a period of decline, divided twice during the next 150 years, and it’s various governments often at war with each other.
Note
During the Ming Dynasty occupation, Confucianism again took root and dramatically changed the Vietnamese state, triggering a seismic shift from Mahayana Buddhism to Confucianism. Officials gradually removed the influence of Buddhism and promoted Confucianism as the foundation of education and social structure at that time. Buddhism did not experience a revival until the 16th century, when the Trịnh Dynasty rose to power and the royal family actively worked to restore its role in Vietnamese society.
The Rise of the Trinh
By the mid-18th century, leaders had mostly defined the borders of what constitutes modern Vietnam, but the last of the great Northern Dynasties was rapidly declining. The preceding century had been turbulent with abundant tales of treachery, warfare, jealousies, greed, injustice and rivalry between the great Houses of Dai Viet and incursion from the southern Chinese states. There is even a great tale of how 300 Vietnamese women helped defeat the Ming by seducing the Naval officers, infecting them with venereal diseases in the process!
In 1620, the head of the House of Nguyễn, Nguyên Phúc Nguyên officially rebuffed the demand for taxes to the court in Hanoi. Leaders rejected several subsequent demands, and in 1627, open warfare finally broke out between the Trịnh in Hanoi and the Nguyễn in Huế. However, the forces in Hanoi failed to secure a victory
As a result, the Trịnh effectively partitioned Đại Việt by taking control of most of the north, while the Nguyễn established their rule over the south.It is particularly significant as this border was very close to the Seventeenth parallel which was ratified as the border between North Vietnam and South Vietnam during the 1954-75 Partition of Vietnam.
Nguyễn Dynasty Period
Throughout most of this period, Hoa Lư remained part of Trường Yên Province in the northern Thanh Hóa state, but it lost much of its influence as the governments in Thăng Long fell into disarray and allowed corruption to spread. When the emergent Nguyễn Dynasty threatened the power of Thang Long, the Northern emperor of the time, Chiêu Thống appealed to the new Qing Dynasty to the north for assistance.
This request was eagerly accepted by the Qing, who sent some 200,000 troops south. Successfully pushing the Nguyen back to the natural “wall” of the Annamite Mountains of Central Vietnam the Qing then took control of Thang Long. And so the fourth domination of Vietnam by China began.
The Nguyen appealed to the French, who had been trying unsuccessfully to gain a foothold in Vietnam since the 17th century. France obliged and the last great Vietnamese feudal administration began with the ascendancy of Gia Long (aka Nguyen Anh) in 1802. With the assistance of French firepower, this first King of the new Nguyen Dynasty took control of all of Vietnam, including the newly annexed southern lands from the fading Champa Empire of Cambodia.
The Rise of Modern Viet Nam
But there is no such thing as a free lunch and the French followed the much same strategy as the Qing had done in the north and over the next few decades, France took control over most of modern day Vietnam. In the process they divided it into the three states of Tonkin, Annam and Cochin – roughly the present day “states’ of North, Central and Southern Vietnam.
The French brought many new and important changes to Vietnam, primarily through the Catholic church. Builders constructed the great cathedrals of Phát Diệm in Ninh Bình and Notre Dame in Saigon in the French style, just as they designed many government and official buildings in the same way. Portuguese and Italian Jesuits and Alexandre de Rhodes codified the Vietnamese language into “chữ Quốc ngữ” – the phonetic alphabet that eventually replaced the traditional Nom system based on Chinese characters.
French monks introduced the humble coffee bean, which has since become an important Vietnamese cash crop and a national icon. However, French rulers governed harshly and remained unpopular, as the fiercely independent Vietnamese people continually resisted their control.
During the subsequent rebellions against the French, followed by the Japanese occupation during WW2 and finally the American-Vietnam war of 1962-75, Hoa Lu remained fiercely loyal to the resistance movement and the ideal of a unified, independent state to rule all of Vietnam.